What is the function of injection mold? What parts does it consist of? What does each do?
What is the function of injection mold? What parts does it consist of? What does each do? The structural composition of the injection molding mold can be divided into the following parts: the molding part, the clamping guide part, the product push-out part, the core extraction part, the heating and cooling part of the mold body, the support part of the mold body and the pouring melt runner, discharge blowhole etc.
(1) Forming part. That is to say, after the mold is assembled and clamped, the component parts of the cavity of the plastic product are directly formed, such as a punch, a concave die, a core, a rod or an insert.
(2) Clamping guide part. It is a component set to make the movable and fixed molds can be correctly aligned with the central axis when the mold is closed, such as guide posts, guide hole sleeves or inclined cones.
(3) Product launch part. It is a component used to push the molded injection product out of the molding die cavity, including ejector rods, fixed plates, push plates and pads.
(4) Core extraction part. When injection molding plastic products with pits or side holes, first extract the core mechanism parts for pit and side hole molding, such as the often used inclined guide posts,
Core-pulling mechanisms such as sliders and curved pins.
(5) The heating and cooling part of the mold body. It refers to a control system that adapts to the temperature of the injection molding process of plastic products, such as resistance heating plates, rods and their electronic control components; circulating cooling water pipes for cooling parts.
(6) The support part of the mold body. Refers to the auxiliary parts to ensure the correct operation of the mold body, such as movable and fixed mold pads, positioning rings, lifting rings and various fastening screws.
(7) Pouring molten material channel. It refers to the flow channel that can lead the molten material injected through the nozzle to the cavity of the forming mold.
(8) Exhaust holes. Refers to the part that allows the air in the mold cavity to be exhausted. Generally, small-sized products do not need to have special vent holes, and the air in the cavity can be discharged from the gaps of each fitting; for large-scale injection molds, vent holes must be provided.
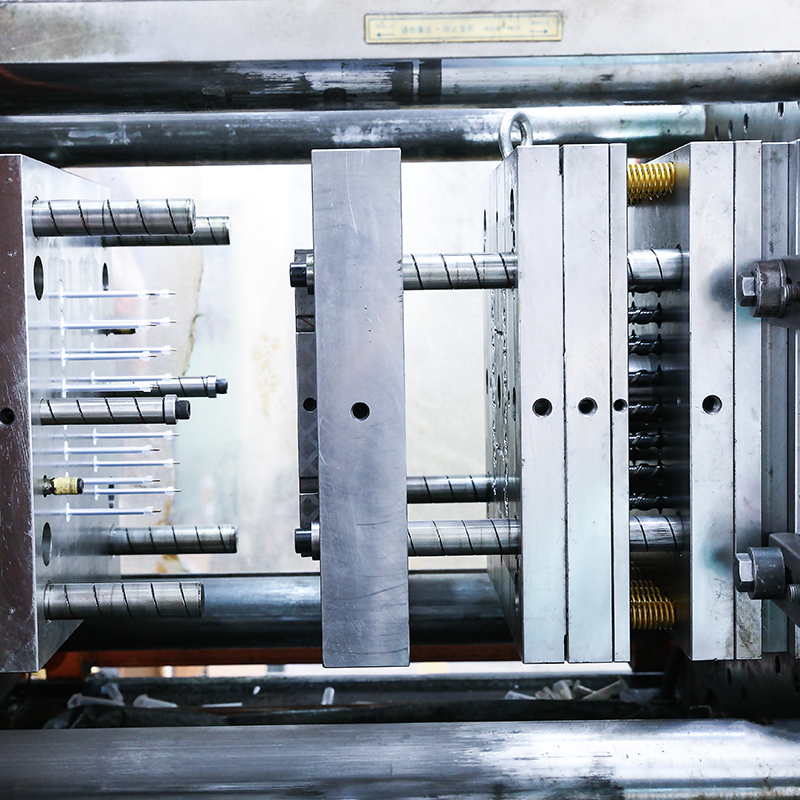 1ml screw vaccine syringe mould
1ml screw vaccine syringe mould
